7.1 Sulphuric acid is a strong acid present in acid rain. It ionises in two steps as follows:
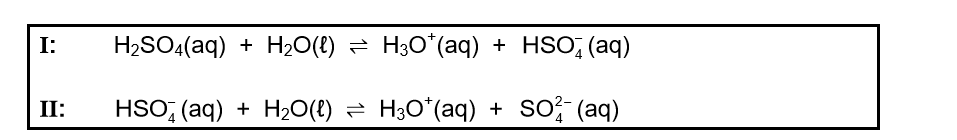
7.1.1 Define an acid in terms of the Lowry-Brønsted theory. (2)
7.1.2 Write down the FORMULA of the conjugate base of H3O+(aq). (1)
7.1.3 Write down the FORMULA of the substance that acts as an ampholyte in the ionisation of sulphuric acid. (2)
7.2 Acid rain does not cause damage to lakes that have rocks containing limestone (CaCO3). Hydrolysis of CaCO3 results in the formation of ions, which neutralise the acid.
7.2.1 Define hydrolysis of a salt. (2)
7.2.2 Explain, with the aid of the relevant HYDROLYSIS reaction, how limestone can neutralise the acid. (3)
7.3 The water in a certain lake has a pH of 5.
7.3.1 Calculate the concentration of the hydronium ions in the water. (3)
The volume of water in the lake is 4 x 109 dm3. Lime, CaO, is added to the water to neutralise the acid according to the following reaction:
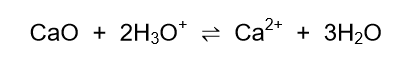
7.3.2 If the final amount of hydronium ions is 1,26 x 103 moles, calculate the mass of lime that was added to the lake. (7)
[20]
