Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions.
Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers
(1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 E.
1.1 The tendency of an atom to attract the bonding pair of electrons is known
as …
A electron affinity.
B electronegativity.
C polarity.
D activation energy. (2)
1.2 Bond length is the average distance between the …
A orbitals of two bonded atoms.
B electrons in two bonded atoms.
C nuclei of two bonded atoms.
D molecules of the same substance. (2)
1.3 Hydrogen bonds and London forces (induced dipole forces) have a common
characteristic in that they …
A are both stronger than chemical bonds.
B both occur between non-polar molecules.
C both occur between polar molecules.
D are both intermolecular forces. (2)
1.4 In order to double the volume of a fixed amount of moles of an enclosed gas,
the temperature in … at constant pressure.
A ºC can be doubled
B K can be doubled
C ºC can be halved
D K can be halved (2)
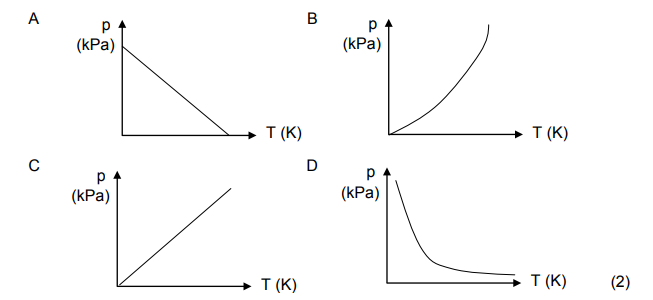
1.5 The graph that CORRECTLY represents the relationship between the
pressure (kPa) and the temperature (K) of an enclosed gas at constant
volume is …
1.6 The solution that will have the greatest concentration of H+ ions if complete
ionisation takes place, is …
A 0,4 dm3 of a 1 mol·dm-3 H2SO4 solution.
B 0,4 dm3 of a 1 mol·dm-3 HCℓ solution.
C 1 dm3 of a 1 mol·dm-3 HCℓ solution.
D 0,4 dm3 of a 1 mol·dm-3 CH3COOH solution. (2)
1.7 Which ONE of the following is NOT a typical reaction of hydrochloric acid?
A It neutralises a base with the release of hydrogen gas.
B It forms hydronium ions in water.
C It colours lithmus paper red.
D It forms CO2 when reacting with a metal carbonate. (2)

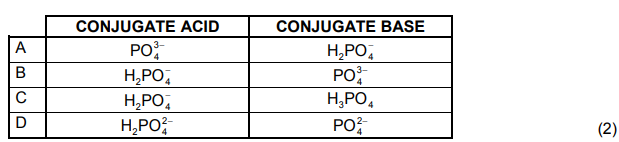
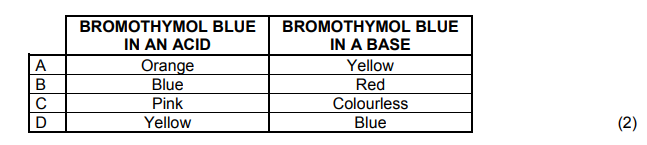
1.9 Which ONE of the following indicates the CORRECT colour of bromothymol
blue in an acid and a base?
1.10 In which ONE of the following reactions is HCℓ oxidised?
A HCℓ(aq) + H2O(ℓ) → H3O+(aq) + Cℓ(aq)
B CaCO3(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) → CaCℓ2(aq) + H2O(ℓ) + CO2(g)
C NH3(aq) + HCℓ(aq) → NH4Cℓ(aq)
D MnO2(aq) + 4HCℓ(aq) → MnCℓ2(aq) + H2O(ℓ) + Cℓ2(g) (2)
[20]
