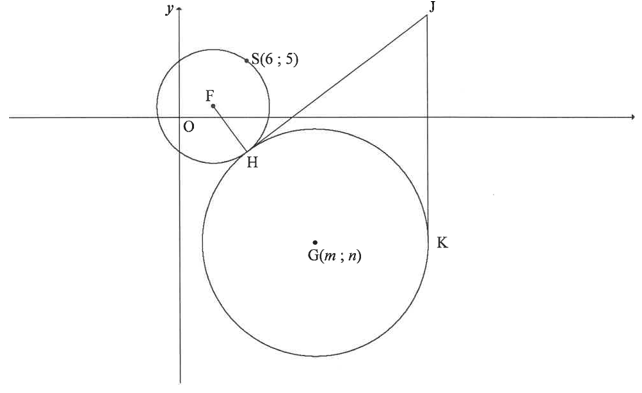
In the diagram the equation of the circle with centre F is (x – 3)2 + (y – 1)2 = r2 .S(6 ; 5) is a point on the circle with centre F. Another circle with centre G(m ; n) in the 4th quadrant touches the circle with centre F, at H such that FH : HG = I : 2. The point J lies in the first quadrant such that FIJ is a common tangent to both these circles. JK is a tangent to the larger circle at K.
4.1 Write down the coordinates of F. (2)
4.2 Calculate the length of FS. (2)
4.3 Write down the length of HG. (1)
4.4 Give a reason why JH = JK. (1)
4.5 Determine:
4.5. I The distance FJ, with reasons, if it is given that JK = 20 (4)
4.5.2 The equation of the circle with centre G in terms of m and n in the
form (x —a) 2 + (y —b)2 = r2 (1)
4.5.3 The coordinates of G, if it is further given that the equation of
tangent JK is x = 22 (7)
[18]