(Start on a new page.)
A pendulum with a bob of mass 5 kg is held stationary at a height h metres above the ground. When released, it collides with a block of mass 2 kg which is stationary at point A.
The bob swings past A and comes to rest momentarily at a position ¼ h above the ground.
The diagrams below are NOT drawn to scale
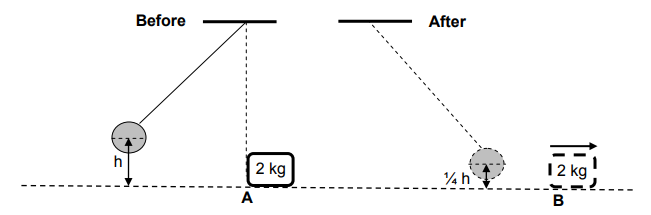
Immediately after the collision the 2 kg block begins to move from A to B at a constant speed of 4,95 m∙s-1. Ignore frictional effects and assume that no loss of mechanical energy occurs during the collision.
5.1 Calculate the:
5.1.1 Kinetic energy of the block immediately after the collision (3)
5.1.2 Height h (4)
The block moves from point B at a velocity of 4,95 m·s-1 up a rough inclined plane to point C. The speed of the block at point C is 2 m·s-1. Point C is 0,5 m above the horizontal, as shown in the diagram below.
During its motion from B to C a uniform frictional force acts on the block.

5.2 State the work-energy theorem in words. (2)
5.3 Use energy principles to calculate the work done by the frictional force when the 2 kg block moves from point B to point C. (4)
[13]
