Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, decomposes to produce water and oxygen according to the following balanced equation:

5.1 The activation energy (EA) for this reaction is 75 kJ and the heat of reaction (ΔH) is –196 kJ.
5.1.1 Define the term activation energy. (2)
5.1.2 Redraw the set of axes below in your ANSWER BOOK and then complete the potential energy diagram for this reaction.
Indicate the value of the potential energy of the following on the y-axis:
• Activated complex
• Products
(The graph does NOT have to be drawn to scale.)

When powdered manganese dioxide is added to the reaction mixture, the rate of the reaction increases.
5.1.3 On the graph drawn for QUESTION 5.1.2, use broken lines to show the path of the reaction when the manganese dioxide is added. (2)
5.1.4 Use the collision theory to explain how manganese dioxide influences the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. (3)
5.2 Graphs A and B below were obtained for the volume of oxygen produced over time under different conditions.
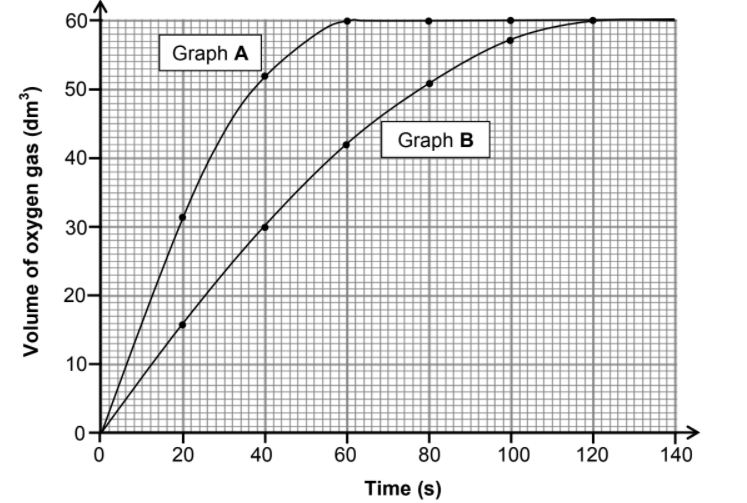
5.2.1 Calculate the average rate of the reaction (in dm3 ∙s-1) between t = 10 s and t = 40 s for graph A. (3)
5.2.2 Use the information in graph A to calculate the mass of hydrogen peroxide used in the reaction. Assume that all the hydrogen peroxide decomposed. Use 24 dm3·mol-1 as the molar volume of oxygen. (4)
5.2.3 How does the mass of hydrogen peroxide used to obtain graph B compare to that used to obtain graph A? Choose from GREATER THAN, SMALLER THAN or EQUAL TO. (1)
5.3 Three energy distribution curves for the oxygen gas produced under different conditions are shown in the graph below.
The curve with the solid line represents 1 mol of oxygen gas at 90 °C.

Choose the curve (P or Q) that best represents EACH of the following situations:
5.3.1 1 mol of oxygen gas produced at 120 °C (1)
5.3.2 2 moles of oxygen gas produced at 90 °C (1)
[20]
